By Staff Correspondent
A slew of sustainable green initiatives taken by DIAL to effectively manage CO2 emissions has made GMR run Delhi Airport – the world’s 5th busiest – one of the greenest airports globally.
Today CO2 emission at Delhi Airport is significantly lower than the significant global airports of its size and capacity, according to a recent study by an online tool Airport Tracker, a joint project by the non-profits International Council on Clean Transportation, ODI, and Transport and Environment.
Airport Tracker intends to reveal “the carbon dioxide emissions generated from aircraft departing worldwide airports.” It contains information for the 1,300 largest global airports, covering 99% of international airline passenger traffic. It shows the total amount of passenger-related emissions generated by each airport.
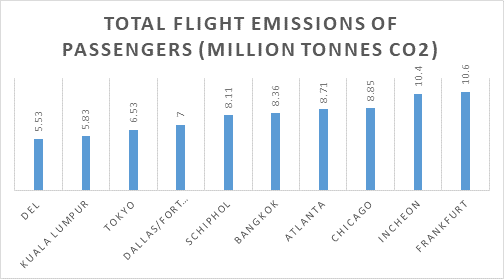
According to the study’s findings, CO2 emission at Delhi Airport is the lowest when compared with any other airport handling over 60 million passengers per annum in the world. Total flight emission by aircraft from Delhi airport is 5.53 million tonnes of CO2, which is significantly lower than some large airports like Singapore’s Changi Airport, South Korea’s Incheon Airport, Germany’s Frankfurt airport and Hong Kong airport, each of which produces over 10 million tonnes of CO2 per annum, according to the Tracker.
Kuala Lumpur Airport followed Delhi Airport with 5.83 million tonnes of CO2 emissions, Tokyo Haneda Airport (6.53 million tonnes of CO2) and Dallas Fort Worth Airport (7 million tonnes of CO2)
DIAL has adopted the globally recognized Airport Council International’s (ACI) Airport Carbon Accreditation framework and thus significantly managed CO2 emission at GMR run Delhi Airport. ACI’s Airport Carbon Accreditation framework is the only global framework for airports that helps airports to inventories and manage their GHG emission effectively
Some of the initiatives adopted by Delhi Airport for reducing Green House Gas (GHG) emission from airport operations include the use of green building concept in construction and operation, use of renewable energy with development of a 7.84 MW solar power plant on the airside.
DIAL has implemented energy-efficient systems and equipment, operational improvement measures such as Airport Collaborative Decision Making (A-CDM), use of low emission technologies such as Bridge Mounted Equipment (BME), Electric vehicles, Fuel Hydrant Systems etc.
Apart from these, Delhi Airport has adopted a green taxiing device — “TaxiBot”. This reduces fuel consumption and emission from airport operations. Delhi Airport is the first airport to adopt this green technology.
Other measures taken by DIAL include using multi-modal connectivity by working closely with all key transportation stakeholders to ensure that all the three terminals of Delhi airport are well-connected by public transportation services, including metro lines.
DIAL has undertaken an airport expansion project to ensure a safe and secure passenger experience and world-class service delivery. As part of the expansion project, Terminal 1 is being redeveloped as per LEED green building standards.
Energy-efficient building materials, electromechanical systems, efficient lighting systems, and double glassed façade are some of the key measures that will reduce electricity consumption and reduce emissions from the Terminal operation.
Delhi Airport is also developing a new elevated Eastern Cross Taxiway (ECT), the first of its kind airport infrastructure in India. This ECT will connect runway 29 and Terminal 1 for aircraft movement, and as per initial estimations, the usage of the ECT will reduce 55,000 tonnes of CO2 annually.
DIAL is currently working towards making Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGIA) “Net Zero Carbon Emission Airport” by 2030 as per the Airport Carbon Accreditation guidelines of Airport Council International (ACI).
In 2020, Delhi Airport will become the first airport in the Asia Pacific region to get Level 4+ (Transition) accreditation, which is the top Level achieved by any airport globally, under the ACI’s Airport Carbon Accreditation Program.
This also certifies that after meeting neutrality requirements, DIAL has also aligned its emission reduction objectives in line with IPCC’s 1.5 Degree scenario.
“Environment Sustainability Management is an integral part of business strategy at Delhi Airport. DIAL has been conducting its business in an environment-friendly and sustainable manner by minimizing the impact of its activities on the environment with necessary pollution control systems and safeguards,” said a DIAL spokesperson.




